Analogue vs Digital Car Meters: Which One is More Accurate?
From tracking speed to monitoring fuel levels, car meters play a vital role in delivering real-time information to drivers. Over the years, vehicle dashboards have evolved from traditional analogue displays to sleek, tech-savvy digital meters. Drivers often debate whether analogue or digital car meters provide better accuracy and reliability
Let’s take a look at how analogue and digital car meters function, their key differences and the factors that impact their accuracy.
Analogue Car Meters: How They Work

Analogue car meters use a mechanical system of gears, a rotating cable and a magnet to display different readings such as speed and fuel level.
In an analogue speedometer, a gear in the transmission rotates a drive cable, which spins a magnet inside the speedometer. This rotation creates a magnetic field that moves a metal disc (speed cup) connected to the needle. The faster the magnet spins, the more the needle moves to indicate speed. The needle’s movement is controlled by a separate spring mechanism.
Digital Car Meters: How They Work
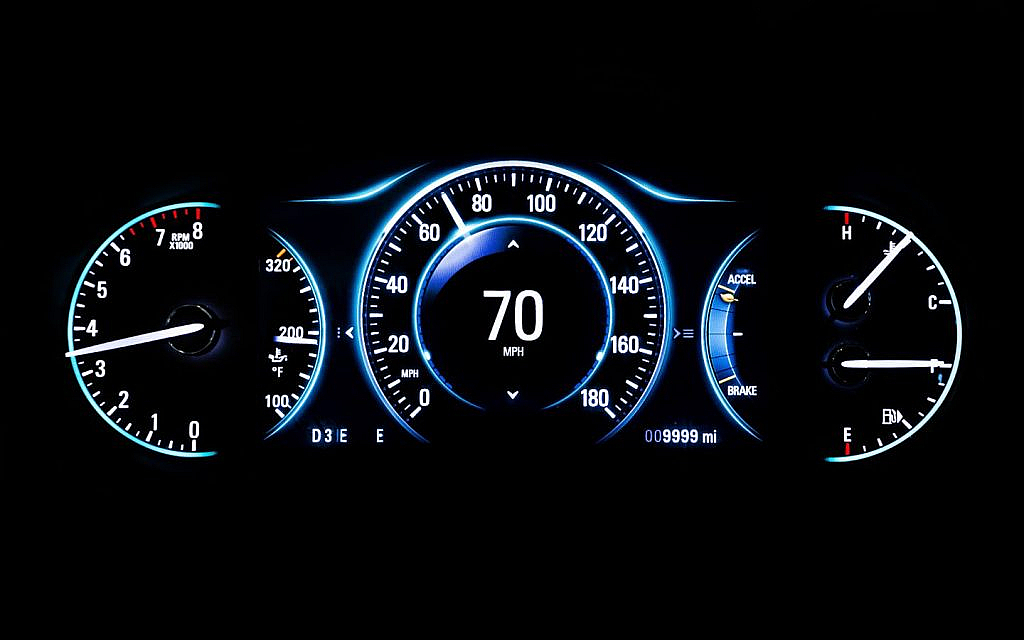
Digital car meters use electronic sensors to measure speed and distance travelled. Magnets are fixed to the vehicle’s outer shaft, with magnetic sensors opposite the shaft. Each time the magnets pass the sensors, they generate an electric pulse.
The pulses are transmitted to the vehicle’s electronic circuit, which processes them to calculate speed and distance. The processed data is displayed as numerical values on an instrument cluster
Comparing the Accuracy of Analogue Vs. Digital Meters
Analogue and digital meters work differently, affecting their accuracy. Understanding how a car speedometer works helps compare its response time and precision.
Let’s explore how both types of car meters differ in accuracy.
Readability and Accuracy
The accuracy of digital vs analogue car speedometers is often compared based on readability. Digital meters show readings in numbers, making them easy to read and reducing the chances of misinterpretation.
Analogue meters use a needle that moves over a dial to indicate readings. That said, the position of the needle and the driver’s viewing angle can make a difference, leading to misinterpretation.
Response Time
Analogue meters are directly connected to the vehicle’s mechanical components. This allows them to respond instantly to speed changes without any processing delay.
Digital meters rely on electronic sensors and data processing which makes them prone to technical errors and delayed information processing.
Durability and Longevity
Analogue meters have mechanical components like gears and needles that move continuously. Over time, these parts can wear out, affecting the metre’s performance.
Digital meters do not have moving parts but rely on electronic circuits and software. Issues like sensor malfunctions or software errors can impact their precision.
Factors That Influence the Accuracy of Analogue and Digital Car Meters.

Various factors, including calibration, environmental conditions and manufacturing quality, can affect digital and analogue car meters. This Analogue vs digital car meters comparison examines the key factors influencing their accuracy.
Calibration and Maintenance
Calibration and maintenance are important to ensure accurate readings for both digital and analogue car meters. Regular calibration ensures accuracy in both meter types. Factors like sensor malfunctions or mechanical wear can impact performance, making speedometer calibration essential for reliable readings.
Environmental Conditions
External factors like temperature and humidity can affect the accuracy of digital vs analogue car speedometers.
Analogue meters have mechanical parts sensitive to vibrations, which may cause slight variations in readings. Extreme heat can cause expansion in these parts, while cold temperatures may stiffen them, affecting movement. Digital meters rely on electronic sensors, which environmental conditions can influence, but they are generally less affected by vibrations. However, extreme temperatures may impact sensor performance and electronic readings.
Manufacturing Quality
The differences between analogue and digital car meters can also be seen in their build quality. Well-built meters with high-quality components provide precise readings and last longer.
Meters made with low-quality materials may wear out faster or show inconsistent readings. Proper design and manufacturing standards help ensure reliable performance over time.
FAQs
What is the difference between analogue and digital car meters?
Analogue meters use mechanical parts like gears and needles, while digital meters rely on electronic sensors to display readings on a screen.
Which type of car meter is more accurate?
Digital meters provide precise numerical readings, but analogue meters offer instant response without processing delays.
Are digital speedometers 100% accurate?
Digital speedometers are generally accurate, but factors like sensor calibration and environmental conditions can cause slight variations.
Both analogue and digital car meters have their working mechanisms and factors affecting accuracy. Analogue meters use mechanical parts, while digital meters rely on electronic sensors.
When comparing analogue vs digital car meters, digital ones offer precise numerical readings, while analogue meters provide instant response. Understanding these differences helps in choosing the right one based on specific needs.
When buying a used car for sale in the UAE, checking the meter’s accuracy is essential. A properly functioning meter ensures reliable speed and fuel readings, helping you make an informed decision.
Stay tuned to the dubizzle auto blogs for more insights on car technology.
Comments
Post a Comment